- Published on
Supercharging AI Agents with MCP Tools
Modern AI Agents are becoming increasingly powerful, but their true potential is unlocked when they can interact with external systems. In my previous post, Building MCP Servers with GitHub Copilot, I discussed how to create MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers and the advantages of using MCP to connect AI models to external tools and data sources vs. traditional function calling.
In this follow-up post, I will dive into using MCP tools with Azure AI Foundry Agents. The complete implementation is available in this aifoundryagent-mcp-tools.
We will create an AI-powered customer service agent for a fictional bike store called Contoso Bike Store. This agent will be capable of handling common customer inquiries such as:
- Checking product availability
- Retrieving product details
- Placing orders
- Tracking order status
Solution Architecture
The agent will handle the inquiries using a MCP server that exposes a set of tools for interacting with the bike store's backend systems.
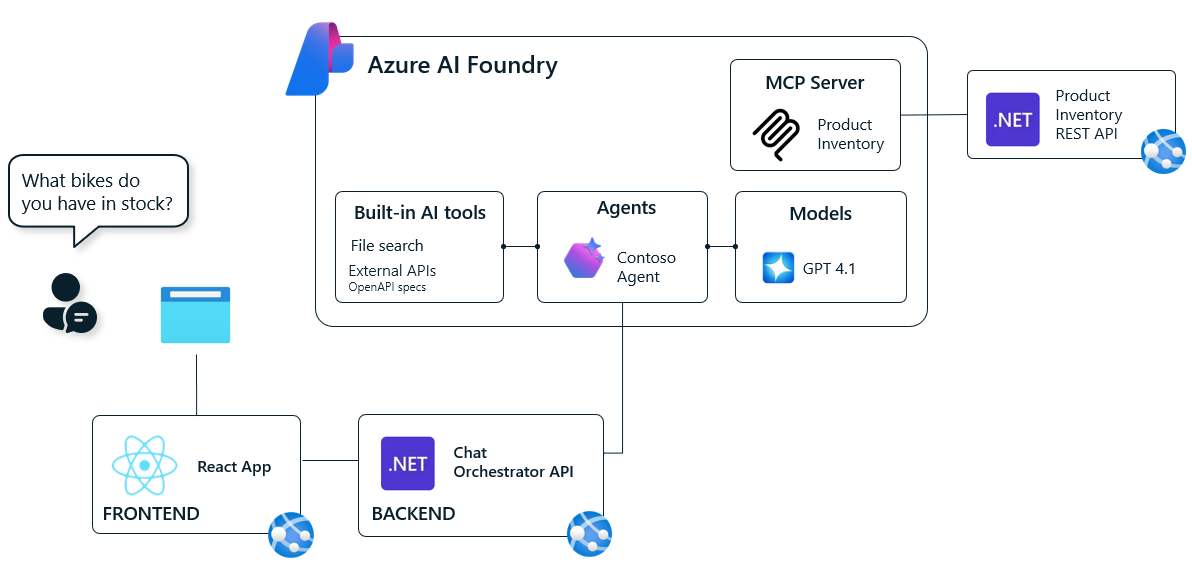
The architecture consists of several key components:
- Frontend: React application hosted on Azure App Service that provides a chat interface for customers
- Backend API: ASP.NET Core Web API (Chat Orchestrator) that processes user prompts and manages agent interactions
- Azure AI Foundry: Hosts the Contoso Agent with access to MCP tools and GPT-4 models
- MCP Server: Custom MCP server that extends agent capabilities with domain-specific tools
- Product Microservice: REST API providing product inventory and order management data
The MCP server is .NET API that connects to a product inventory microservice to fetch bike data. The order management tools are simulated for demonstration purposes.
The frontend provides a simple chat interface where users can interact with the Contoso Bike Store assistant. The backend API orchestrates the communication between the frontend, the Azure AI Foundry agent, and the MCP server. The Agent uses GPT-4.1 model and has access to the MCP tools for real-time data retrieval and order processing.
Pre-requisites & Setup
The Readme file in the GitHub repository aifoundryagent-mcp-tools provides detailed setup instructions. In summary, you will need:
- An Azure account with permissions to create resources
- Local development environment or use CodeSpaces
- Deploy the infrastructure using Azure Developer CLI (
azd) which provisions:- Shared resources (Azure Key Vault, App Service Plan, Application Insights, Storage Account)
- AI Foundry resources (AI Foundry project, models)
- Azure App Service for frontend and backend
- Azure App Service for MCP server
Running the Contoso Bike Store Agent
After deploying the solution using azd up, you can grab the web application URL from the output to access the chat interface.
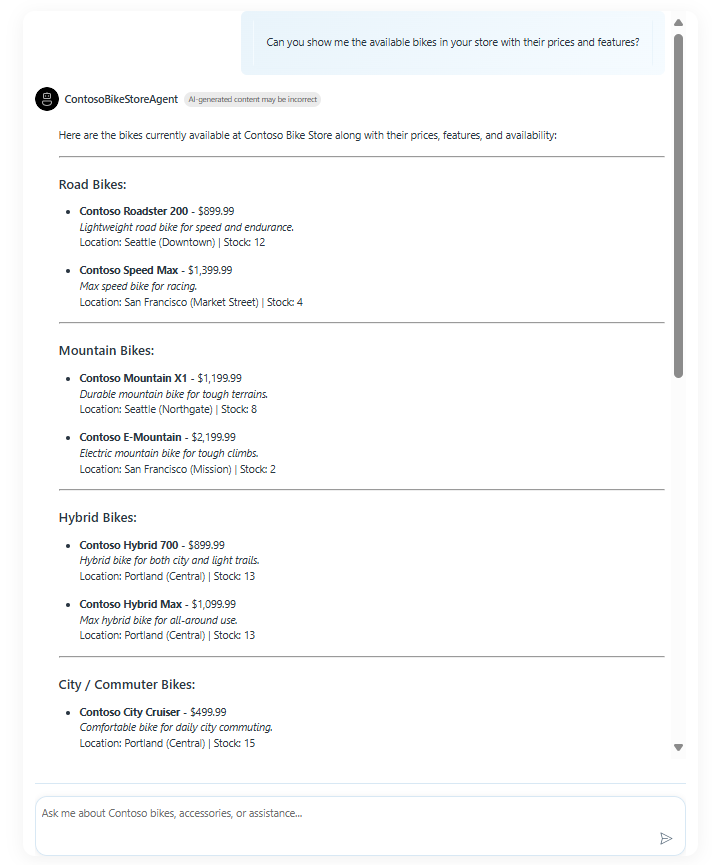
The Contoso Bike Store agent is pre-configured with a set of tools that allow it to interact with the MCP server. You can ask questions like:
- "What bikes are available in your store?"
- "What is the price of the Mountain Explorer bike?"
- "What is the status of my order ORD-1234?"
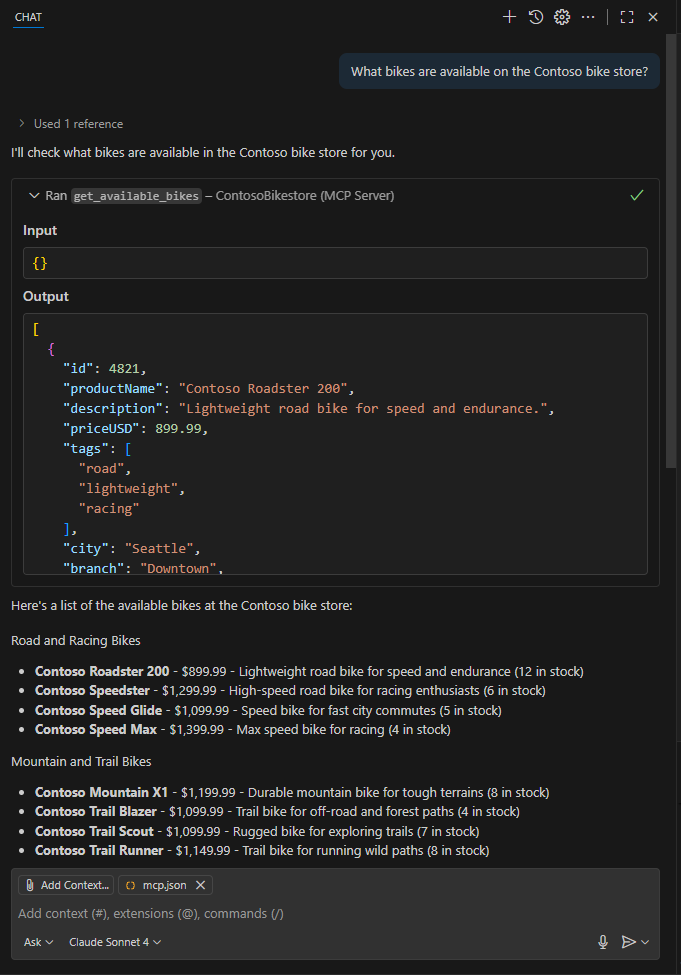
Testing the MCP Server on Github Copilot Chat
You can also test the MCP server directly using GitHub Copilot Chat in VS Code.
Add the MCP server URL (e.g., https://<your-mcp-server>.azurewebsites.net) in MCP server server settings. You will create a new folder .vscode in your workspace and add a mcp.json file with the following content:
{
"servers": {
"ContosoBikestore": {
"type": "sse",
"url": "https://<your-mcp-server>.azurewebsites.net/sse",
"headers": {
"X-API-KEY": "[Your MCP Server API Key]"
}
}
}
}
Refer to the Use MCP servers in VS Code documentation for setting up MCP servers in VS Code.
After configuring the MCP server, you can start a new chat in Copilot Chat.
Understanding the Execution Flow
When you send a message to the agent, here's what happens behind the scenes:
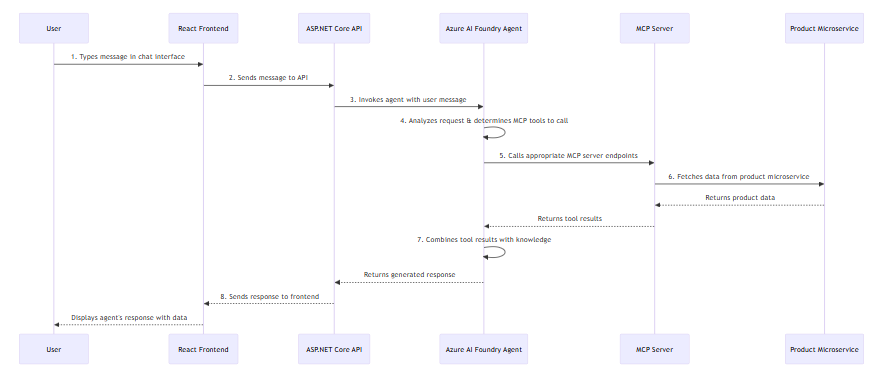
- User Input: User types a message in the chat interface
- Frontend to Backend: The React app sends the message to the ASP.NET Core API
- Agent Invocation: The backend calls the Azure AI Foundry agent with the user query
- Tool Decision: The agent analyzes the request and determines which MCP tools to call
- MCP Tool Execution: The agent calls the appropriate MCP server endpoints
- Data Retrieval: The MCP server fetches data from the product microservice
- Response Generation: The agent combines the tool results with its knowledge to generate a helpful response
- Display Result: The frontend displays the agent's response with any relevant data
Implementation Details
Let us now explore how the solution is implemented in more detail.
Contoso Bike Store MCP Server
The MCP server uses ModelContextProtocol .NET SDK to define and expose tools. You would also need to add references to ModelContextProtocol.AspNetCore to expose the MCP server over HTTP.
Here's how the MCP server is registered in the ASP.NET Core application:
using ContosoBikestore.MCPServer.Tools;
using ContosoBikestore.MCPServer.Authentication;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add Application Insights telemetry collection
builder.Services.AddApplicationInsightsTelemetry();
// Register HttpClient for DI
builder.Services.AddHttpClient();
builder.Services
.AddMcpServer()
.WithHttpTransport() // HTTP transport for Azure integration
.WithTools<ProductInventoryTool>()
.WithTools<OrderManagerTool>();
// Configure API Key authentication for security
string apiKeyHeaderName = builder.Configuration["ApiKey:HeaderName"] ?? "X-API-KEY";
builder.Services.AddAuthentication(builder =>
{
builder.DefaultAuthenticateScheme = ApiKeyAuthenticationOptions.DefaultScheme;
builder.DefaultChallengeScheme = ApiKeyAuthenticationOptions.DefaultScheme;
}).AddScheme<ApiKeyAuthenticationOptions, ApiKeyAuthenticationHandler>(
ApiKeyAuthenticationOptions.DefaultScheme,
options => options.ApiKeyHeaderName = apiKeyHeaderName);
var app = builder.Build();
app.Run();
Product Inventory Tools
The product inventory tools demonstrate how to connect MCP to external data sources. In our solution, we connect to a product microservice that provides bike inventory data.
The tools have an attribute [McpServerToolType] to register them with the MCP server. Each tool method is decorated with [McpServerTool] and includes a [Description] attribute to provide metadata for the AI model. The description helps the model understand the purpose of each tool and when to use it.
[McpServerToolType]
public sealed class ProductInventoryTool
{
private readonly HttpClient _client;
private readonly ILogger<ProductInventoryTool> _logger;
private readonly string _baseUrl;
public ProductInventoryTool(HttpClient client, ILogger<ProductInventoryTool> logger)
{
_client = client;
_logger = logger;
_baseUrl = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("CONTOSO_STORE_URL");
}
[McpServerTool]
[Description("Get all available bikes from the Contoso bike store")]
public async Task<string> GetAvailableBikes()
{
try
{
var response = await _client.GetAsync($"{_baseUrl}/api/bikes");
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
var content = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
return content;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error fetching available bikes");
return "Error: Unable to fetch available bikes at this time.";
}
}
[McpServerTool]
[Description("Get details for a specific bike by its ID")]
public async Task<string> GetBikeById(
[Description("The ID of the bike to retrieve")] int bikeId)
{
try
{
var response = await _client.GetAsync($"{_baseUrl}/api/bikes/{bikeId}");
if (response.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.NotFound)
{
return $"Bike with ID {bikeId} not found.";
}
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
var content = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
return content;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error fetching bike {BikeId}", bikeId);
return $"Error: Unable to fetch bike details for ID {bikeId}.";
}
}
}
Authentication to the MCP Server
The MCP server is similar to any other web API and hence you can use the same authentication mechanisms. In this example, we use a simple API key authentication to secure access to the MCP server. The API key is passed in the X-API-KEY header of each request.
Contoso Bike Store Agent
The backend API (Chat Orchestrator) is responsible for invoking the Azure AI Foundry agent and passing user prompts. The backend API creates a agent in Azure AI Foundry with access to the MCP server for tool calls.
The agent uses GPT-4.1 model and is configured with a system message that defines its role and behavior. The system message also includes instructions on how to use the MCP tools effectively.
Also note that the MCP tool call would require approval workflow. In this example, we automatically approve all MCP tool calls for simplicity. In a production scenario, you may want to implement selective approval based on the tool being called.
private async Task<PersistentAgent> GetOrCreateAgentAsync(string agentName, string? agentId)
{
// Configure the MCP tool connection
var mcpServerUrl = Config.CONTOSO_STORE_MCP_URL;
var mcpServerLabel = Config.CONTOSO_STORE_MCP_SERVER_LABEL;
MCPToolDefinition mcpTool = new(mcpServerLabel, mcpServerUrl);
// Create agent with MCP tool access
agentDefinition = await _projectClient.Administration.CreateAgentAsync(
modelId,
name: agentName,
instructions: agentInstructions,
tools: [mcpTool]);
return agentDefinition;
}
private async Task InvokeAgent(string userPrompt, PersistentAgent agent, PersistentAgentThread thread, ILogger logger)
{
// Configure MCP tool resources with authentication
var mcpServerLabel = Config.CONTOSO_STORE_MCP_SERVER_LABEL;
MCPToolResource mcpToolResource = new(mcpServerLabel);
mcpToolResource.UpdateHeader("X-API-KEY", Config.CONTOSO_STORE_MCP_SERVER_API_KEY);
ToolResources toolResources = mcpToolResource.ToToolResources();
// Create message and run the agent
var message = _projectClient.Messages.CreateMessage(
thread.Id, MessageRole.User, userPrompt);
ThreadRun run = _projectClient.Runs.CreateRun(thread, agent, toolResources);
// Handle tool approval workflow
while (run.Status == RunStatus.RequiresAction)
{
if (run.RequiredAction is SubmitToolApprovalAction toolApprovalAction)
{
var toolApprovals = new List<ToolApproval>();
foreach (var toolCall in toolApprovalAction.SubmitToolApproval.ToolCalls)
{
if (toolCall is RequiredMcpToolCall mcpToolCall)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Approving MCP tool call: {mcpToolCall.Name}");
toolApprovals.Add(new ToolApproval(mcpToolCall.Id, approve: true));
}
}
if (toolApprovals.Count > 0)
{
run = _projectClient.Runs.SubmitToolOutputsToRun(thread.Id, run.Id, toolApprovals: toolApprovals);
}
}
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(1000));
run = _projectClient.Runs.GetRun(thread.Id, run.Id);
}
}
Key Takeaways and Best Practices
Keep Tools Focused: Each MCP tool should have a single, well-defined responsibility. This makes them easier to test, maintain, and reuse across different agents.
Handle Errors Gracefully: Always include proper error handling in your MCP tools. The agent should receive meaningful error messages that help it provide useful feedback to users.
Use Descriptive Metadata: The
[Description]attributes on your tools and parameters are crucial - they help the AI model understand when and how to use each tool effectively.Implement Authentication: In production environments, always secure your MCP servers with proper authentication mechanisms like API keys or OAuth.